Proactive Health Strategies for Animal Companions
Ensuring the well-being of animal companions involves more than just reactive treatment when illness strikes. A proactive approach to pet health focuses on preventative measures, early detection, and creating an environment that supports physical and mental vitality. This strategy encompasses various aspects, from regular veterinary visits to appropriate nutrition and enriching daily activities, all contributing to a longer, healthier life for our beloved animals.

Understanding the Importance of Regular Veterinary Care
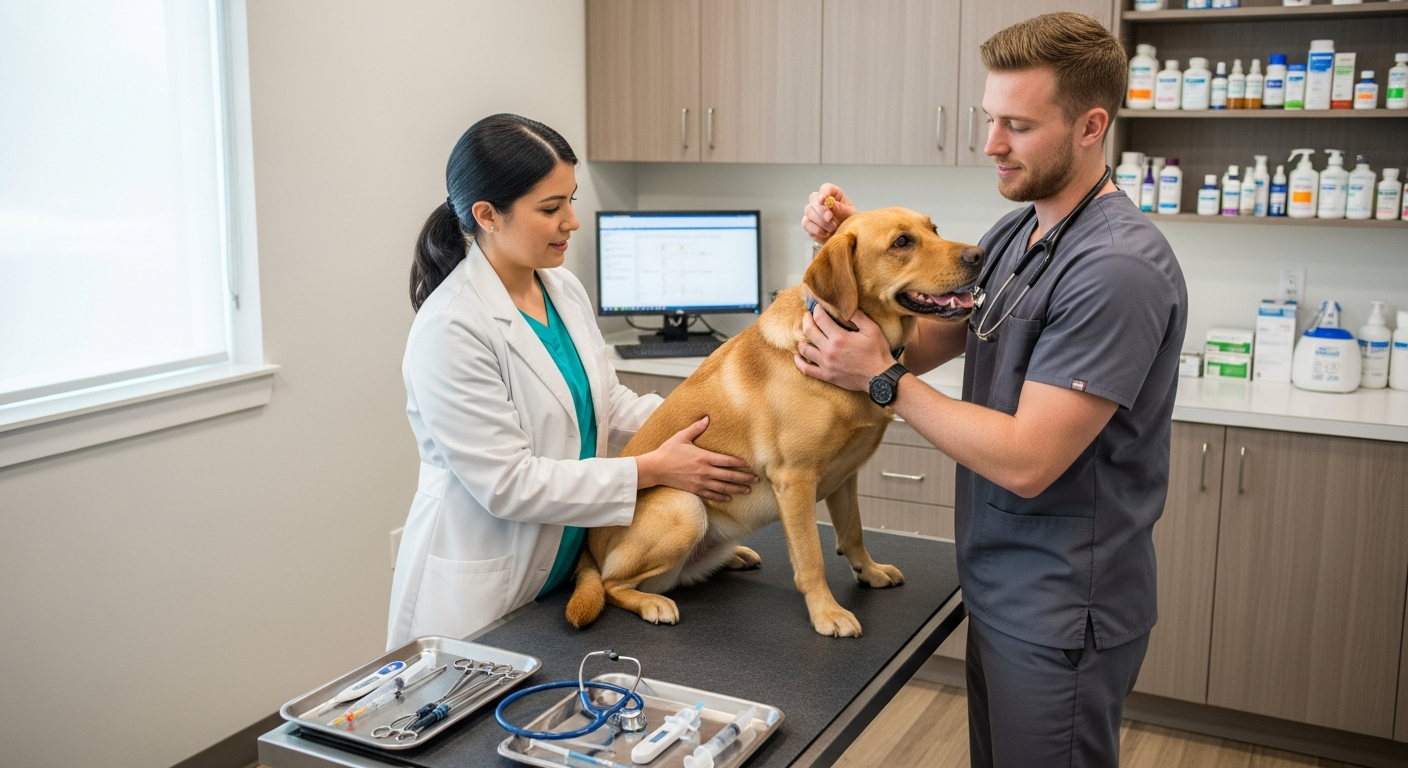
Routine veterinary care forms the cornerstone of proactive health management for any animal companion. Regular check-ups allow veterinarians to monitor an animal’s overall health, detect potential issues early, and provide essential preventative treatments. This includes vaccinations against common diseases, which are crucial for protecting animals from preventable illnesses, especially those that can be severe or even fatal. A consistent schedule of check-ups helps establish a baseline for your animal’s health, making it easier to identify deviations.
Beyond vaccinations, preventative care also involves consistent parasite control. This includes treatments for fleas, ticks, heartworms, and intestinal parasites, which can cause significant health problems and discomfort for domestic animals. Discussing appropriate parasite prevention strategies with a veterinary professional ensures that your companion is protected year-round, tailored to their specific species, lifestyle, and local environmental risks. Early intervention through regular vet visits can significantly improve an animal’s welfare and quality of life.
Essential Nutrition for Animal Welfare
Proper nutrition is fundamental to an animal’s health and welfare. A balanced diet tailored to the specific species, age, breed, and activity level of your companion is crucial. High-quality food provides the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals to support immune function, maintain a healthy weight, and contribute to overall vitality. Understanding the dietary needs of different animal species, whether a cat, dog, bird, or small mammal, is key to preventing nutritional deficiencies or excesses that can lead to health issues.
Selecting appropriate food involves reading labels carefully and consulting with veterinary experts. Factors such as protein content, fat levels, and the presence of essential fatty acids or specific dietary supplements can significantly impact an animal’s health. Avoiding common pitfalls like overfeeding, feeding human foods not suitable for pets, or providing diets lacking essential nutrients are vital steps in ensuring optimal nutrition. A well-nourished animal is better equipped to resist illness and maintain an active lifestyle.
Promoting Positive Behavior and Training
Behavioral health is as important as physical health for an animal companion’s overall well-being. Early socialization and consistent, positive training can prevent many common behavioral problems and strengthen the bond between humans and their animals. For domestic animals, learning appropriate behaviors helps them integrate better into family life and reduces stress for both the animal and its caregivers. This proactive approach to behavior management creates a more harmonious living environment.
Training techniques that focus on positive reinforcement are highly effective in shaping desired behaviors and building confidence in animals. Addressing behavioral concerns promptly, such as excessive barking, destructive chewing, or aggression, can prevent them from escalating into more serious issues. Understanding the natural behavior patterns of your particular species of animal companion allows for more effective training and enrichment strategies, contributing significantly to their mental health and overall quality of life.
Creating an Enriching Habitat for Domestic Animals
An enriching habitat is crucial for the physical and mental health of animal companions. This involves providing an environment that meets their specific needs for space, safety, and stimulation. For domestic animals, this might mean a secure yard, comfortable bedding, and access to appropriate toys and climbing structures. Environmental enrichment helps prevent boredom, reduces stress, and encourages natural behaviors, which are all vital for their welfare.
Ensuring that an animal’s living space is clean, safe, and stimulating contributes significantly to their health. This includes providing opportunities for regular exercise, mental challenges through puzzle toys, and appropriate social interaction. The design of their habitat should consider the species’ natural instincts and requirements, such as opportunities for digging, chewing, or perching, depending on the animal. A well-designed and enriching habitat supports an animal’s physical conditioning and psychological well-being.
Protecting Your Companion’s Health Through Environmental Awareness
Protecting an animal companion’s health also involves being aware of potential environmental hazards within the home and local ecosystem. Many common household products, plants, and human foods can be toxic to animals. Proactive measures include securing harmful substances, identifying toxic plants, and ensuring outdoor spaces are free from dangers like pesticides or antifreeze. This protective mindset extends to understanding potential risks in the wider environment.
Considering the broader ecosystem, responsible pet ownership also means preventing your domestic animal from negatively impacting local wildlife and vice versa. For instance, keeping cats indoors or in secure enclosures can protect them from outdoor dangers and prevent them from preying on local birds and small mammals. Awareness of local disease outbreaks or environmental toxins in your area can also inform preventative health strategies, such as avoiding certain walking paths during peak parasite seasons or after pesticide applications, ensuring the continued health and protection of your animal companion.